What is hepatitis C?
An RNA virus called hepatitis C causes infection and associated inflammation in the liver. This disease caused by the hepatitis C virus is called hepatitis C disease. This disease is a contagious infectious disease and when left untreated, it damages the liver over the years, causing cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C disease is either asymptomatic at first (in the acute period) or shows insignificant symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and indigestion that can be seen in many diseases. Therefore, it is very difficult to diagnose the disease in the initial period.
How does hepatitis C progress?
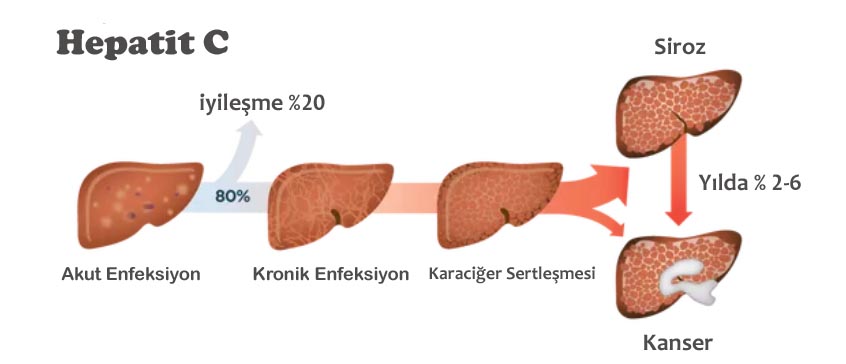
From the moment the hepatitis C virus enters the body, it is called the acute period, this period lasts for 6 months and usually does not show any symptoms. Acute hepatitis C infection in 75-85% of patients turns into a chronic one. Chronic Hepatitis C is a lifelong disease that can lead to cirrhosis, liver cancer and even death by insidiously progressing in the following years.
Acute Hepatitis C
If hepatitis C disease lasts for 6 months or less, it is called Acute Hepatitis C. Acute Hepatitis C can turn into chronic if not treated in time.
Approximately 15-25% of acute hepatitis C patients can recover from the infection without treatment. These people can contract and recover from chronic hepatitis C without even knowing they are sick.
Chronic hepatitis C
If hepatitis C disease lasts for more than 6 months, it is called Acute Hepatitis C. Chronic hepatitis can last for years because it is very difficult for the body to get rid of this virus. About 20% of people with hepatitis C experience problems with the thyroid, intestines, eyes, joints, blood, spleen, kidneys and skin. It has been found that about 85% of patients infected with the hepatitis C virus cannot get rid of the virus, and as a result, they develop a long-term liver infection called chronic hepatitis C.
Chronic hepatitis C disease can cause cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is the last stage of liver damage caused by various factors. In approximately 20% of chronic hepatitis C patients, liver damage may occur over time and liver cirrhosis may occur within 15-20 years. In cirrhosis, the liver is so destroyed that it can no longer renew itself. This can lead to various health problems, including fluid buildup in the abdomen and bleeding from a vein in the esophagus.
When the liver is unable to filter out toxins, toxins, toxic wastes can build up in the bloodstream and damage brain functions. People with liver cirrhosis have an increased risk of developing liver cancer. Cirrhosis is more common in people who consume alcohol.
What are the Symptoms of Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C does not show symptoms until it damages the liver. It is an insidious disease that progresses silently, and most of the patients do not experience any symptoms.
The most common symptoms experienced by hepatitis C patients are:
- Extreme fatigue
- Anorexia
- Jaundice. Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes
- Itchy skin
- Swelling in the abdomen with fluid accumulation in the abdomen
- Swelling in the legs
- Easy bleeding on the skin
- Involuntary weight loss
- Easy bruising of the skin
- Dysfunction of the liver
- Diarrhea
- Dark urine
- Light colored stool
- Pain and tenderness in the liver area
- Low grade fever
- Spider angiomas, spider-like blood vessels that develop in the skin
- Joint pains
- Nausea, vomiting
- Abdominal pain
How is Hepatitis C Transmitted?
From a person carrying the hepatitis C virus, i.e. through a blood transfusion
Having unprotected sex with a hepatitis C patient
Shared use of personal care tools such as razor blades with a person with hepatitis C
Stinging of a needle contaminated with the hepatitis C virus
Common syringe use
Hepatitis C virus can be passed from pregnant mother to baby
Hepatitis C is not transmitted through breast milk. However, if the mother’s breast is cracked and bleeding due to breastfeeding, it can pass to the baby through the blood.
Organ transplantation can also cause transmission of the hepatitis C virus.
Tattooing, using piercings, acupuncture needle treatment can also lead to the transmission of hepatitis C disease.
Hepatitis C is not transmitted by coughing or sneezing.
Does hepatitis C kill?
In case of chronic hepatitis C disease, there is a risk of developing chronic hepatitis first, then liver cirrhosis and liver cancer over the years, and it should be known that hepatitis C is a deadly disease.
What is a hepatitis C carrier?
People who have the hepatitis C virus in their body but are not treated because they do not show any symptoms and are likely to transmit the virus to others are called. People who are carriers of this disease should stay under regular doctor follow-up and have liver function tests done twice a year.
HCV RNA PCR Hepatitis C Test
It is the test used to confirm HCV positive screening results. Anti-HCV screening test should be done if positive. It is also used in the follow-up of chronic disease.
When anti-HCV positivity is detected, further tests are performed. To confirm positivity, WB-based LIA (Line-immunoblot tests) and HCV RNA should be screened by PCR. In case of positivity with LIA, HCV RNA should be tested by PCR. If HCV RNA PCR is positive, it indicates that the patient is acutely infected with HCV, and if HCV RNA PCR is negative, the patient has been exposed to the agent but is chronically infected.
Hepatitis C can be detected with a simple blood test. This test indicates the number of anti-HCV antibodies in the blood. This test is called a second generation enzyme immunoassay (EIA-2). Another test is done by PCR method to confirm the diagnosis. The other name of the test performed by the PCR method is the HCV RNA PCR test. A positive HCV RNA test indicates that you have hepatitis C, and a negative test indicates that you do not have hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C Vaccine
There is no vaccine available to prevent hepatitis C disease. However, scientists continue to work on making the hepatitis C vaccine. Doctors usually recommend hepatitis C patients to be vaccinated against hepatitis A and hepatitis B.