Genital Wart
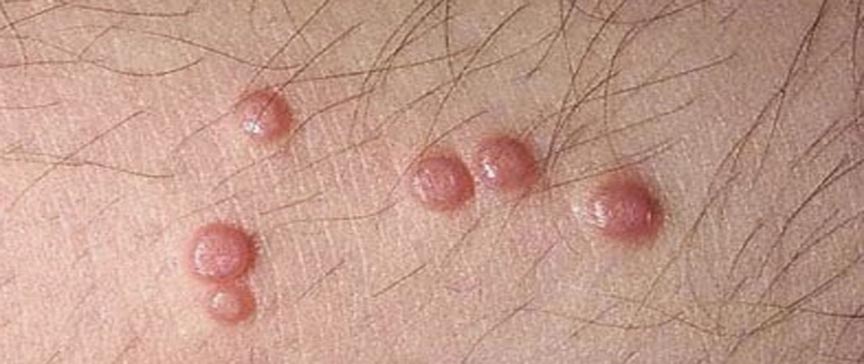
Genital warts are an indication of infection in 1% of sexually active adults. Large, moist, pedunculated soft papillomas located on the external genital surfaces, perineum, inner vaginal surface, penis and anus; condyloma acuminatum is called by names such as anogenital warts and exophytic warts. In addition, flat warts (genital warts) are called condyloma planum. 90% of genital wart are caused by HPV Types 6 and 11, which are known as low-risk types, and although the risk of progression to malignancy is low, they are responsible for approximately 9-12% of CIN cases.
What is Genital Wart? How is it found?
The incubation period of genital warts is 1-6 months, and the maximum virus concentration in the lesions is 6 months. Genital warts may appear between a few weeks and several years after the virus is taken into the body, or they may not appear at all. This makes it difficult to determine when and to whom HPV may be transmitted. For this reason, it is necessary to have an HPV Test.
Genital warts may regress spontaneously in 3-4 months or may increase in number and/or size. Especially during pregnancy, due to hormonal changes, warts may increase in number and size, bleed, or in very rare cases make vaginal delivery difficult. Spontaneous regression is observed in 50% of condylomas observed in pregnant women within 3 months of delivery.
Genital Wart Symptoms and Treatment Methods
In the traditional treatment of genital warts, cryotherapy, 50-80% bi/trichloroacetic acid solution, podofilox 5% solution and gel, which should be applied only on the lesion without contaminating the healthy tissue by the patient, and 10-25% podophylline applied by the physician are used. The use of both podofilox and podophylline is contraindicated in lesions of the cervix, urethral meatus, vagina and anus, and in pregnant women. LEEP (Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure) and laser are applied in the treatment of genital condylomas that have spread over large areas. Although the treatment rate exceeds 90% with the application of these methods, the virus may remain latent in the person and may form a lesion again.
It is thought that the removal of warts as a result of treatment reduces the risk of sexual transmission and progression to cancer, but does not completely eliminate both risks. The risk of recurrence of genital warts is high, especially in the first three months after treatment. It is not known how long the virus remains in the body after the treatment of genital warts.
Genital Wart Prices 2025
Call now for information about genital warts cost 2025.
instagram: labistanbul