Coenzyme Q10 ( Ubiquinone )
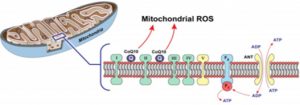
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) functions as an electron carrier in oxidative phosphorylation, known as aerobic respiration, which takes place in the cell’s mitochondria organelle. Also known as ubiquinone, its reduced form is ubiquinol. While ubiquinone plays a role in energy metabolism, ubiquinol is important for antioxidant functions. Biochemically, it is a fat-soluble compound. It is found in all cell membranes and is carried in the circulation by lipoproteins.
Because it can be found in both reduced and oxidized form in the body, it is important for oxidant–antioxidant systems. In terms of these systems, it is important not only the amount but also the present amount in reduced or oxidized form. Thanks to its redox potential, it plays a role in controlling the oxygen radicals it produces during the body’s energy synthesis.
Antioxidant systems necessary for the stability of membranes, energy conversion of cells and ATP production are indispensable for the continuation of cell viability. Coenzyme Q10 is an inevitable molecule to ensure the continuity of these events. ATP is the body’s only usable unit of energy and is not stored in the body. For this reason, it must be synthesized from carbohydrates, fats and proteins continuously and regularly.
The survival of cells is limited to seconds if their synthesis stops. The most important mechanism that provides adequate and regular synthesis of ATP is the electron transport chain stage of oxidative phosphorylation, which we know as aerobic respiration. Coenzyme Q10 has a vital role in the healthy functioning of this chain.
Many factors can affect the blood level of coenzyme Q10;
CoenzymeQ10 has been offered as a nutritional supplement for many years because it can reduce the level of these and similar factors. Although it is stated in the promotions of commercial samples that they can support treatment or play a role in the prevention of many diseases, there are not enough scientific studies on these issues. Therefore, it is necessary to be careful when using it as a support. It is beneficial to take it by following the level with laboratory tests.
In some scientific studies, low coenzyme Q10 levels have been found to be associated with chronic heart disease and it has been stated that coenzyme Q10 supplementation may be protective for chronic heart disease.
It has been suggested that three mechanisms underlie this protective effect;
In another study (Rosenfeldt), it is emphasized that the addition of Coenzyme Q10 as a support to traditional hypertension treatment would be a rational choice in lowering blood pressure.
When Coenzyme Q10 is taken from the outside for support, it is not very important in what form it is. Because if taken in the form of ubiquinol, it is converted to ubiquinone before it reaches the absorption cells of the small intestine.
Coenzyme Q10 test
The use of statin-derived drugs to treat high cholesterol level in patients with suspected mitochondrial disorder, treatment of degenerative brain diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease Coenzyme Q10 test is recommended during follow-up.
It is important to monitor the level of statin type drugs, especially since they reduce their synthesis.
Primary coenzymeQ10 deficiency is an extremely rare disease. However, since it occurs with neurological symptoms such as seizures, growth retardation, loss of balance, and muscle weakness, it should be measured in patients with these findings.
Although the plasma level does not always show the same change as the tissue level, it is useful to measure the plasma level in order to evaluate the bioavailability of exogenously administered coenzyme Q10.
Coenzyme Q10 measurement
General methods for the evaluation of CoQ10 in plasma and biological tissues are based on alcohol-hexane extraction. The sample thus obtained is injected into a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) device and is quantitatively measured with a UV detector at 275 nm or with an electrochemical detector. In addition, there are kits that measure with the enzyme immunoassay technique.
People who use external coenzyme Q10 (Ubiquinone) or its reduced form ubiquinol support can have a coenzyme Q10 test done, as can be requested by the physician they are followed for the patients. Only one blood sample will be taken from the person who will have the test. Therefore, it does not contain any difficulties or risks.
CoenzymeQ10 was first discovered by Frederick Crane and his colleagues at the University of Wisconsin-Madison in 1957. It was in the 1990s that it could be used as a commercial form with the contribution of different scientists and research companies.